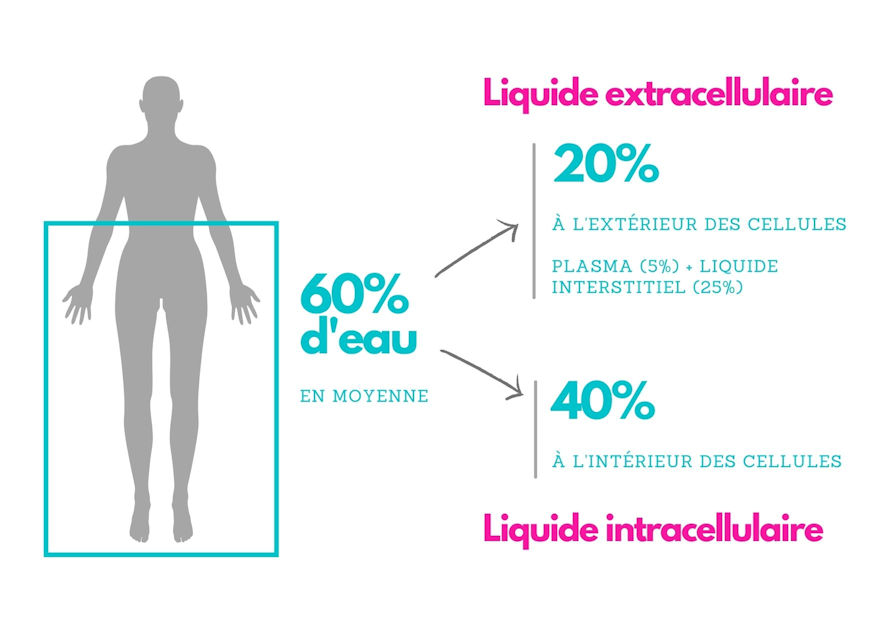
Our body is made up of approximately 60% water (more or less depending on age and muscle and fat content). All our cells are immersed in a water-rich environment (called extracellular fluid), and their interior is also composed of water (called intracellular fluid). It is therefore essential to drink water of good quality and in sufficient quantity for the proper functioning of our body.. Indeed, cellular and tissue dehydration contributes to the clogging and acidification of the body, creating a favorable environment for inflammation and the development of diseases. Water is indeed essential for the excretory organs.1 the main ones being the intestines and the kidneys in their elimination process.
What about so-called "drinking" water?
The potability of water today is based on several criteria, including physico-chemical parameters (pH, temperature, ionic composition, presence of undesirable elements such as pesticides, etc.), organoleptic properties (taste, odor, color), and microbiological factors (various pathogens). Potable water is defined as "water that can be drunk or used for domestic and industrial purposes without health risk." However, this does not necessarily mean that water without health risks is beneficial for health. This definition should introduce the concept of ""First, do no harm"", that is to say, not to harm health, a concept dear to Hippocrates, the father of natural, non-intrusive medicine. Thus, the previously stated criteria for potability do not take into account micropollutants (pharmaceutical and hormonal residues), the synergies between certain pollutants that produce "cocktail effects" (chlorine, nitrates, pesticides, etc.), or the bioaccumulation in the body of substances present in low doses in water, such as endocrine disruptors.
It is therefore recommended to avoid drinking tap water and to prefer the consumption of quality water, "biocompatible" according to Vincent's bioelectronics2It seems like your message is incomplete. Could you please provide the text you would like translated from French to English?
pure (without bacteria),
Slightly acidic pH (between 6 and 7),
"non-oxidized nor oxidizing (rH2)"3 less than 28),
as low in minerals as possible (dry residue less than 120 mg/L) to avoid burdening the body with non-assimilable minerals.
Chlorine, widely used to destroy bacteria in tap water, is a very powerful oxidant (rH2 close to 42). It is worth noting that humans are more bacterial than cellular beings... which raises questions about consuming chlorinated water! Furthermore, chlorine can combine with other compounds present in the water and create by-products such as chloramine and trihalomethanes, some of which are classified as "possible carcinogens" (group 2B) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Several studies indeed suggest a link between certain trihalomethanes and various cancers, including colon cancer.4, and of the pancreas5.
But then, which water should we drink?
We will avoid bottled water in plastic, which has little vitality and is contaminated by tiny plastic particles (polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) in particular).6, with harmful consequences for our health. Indeed, an American study showed that out of 259 plastic water bottles purchased in 9 different countries and from 11 different brands, 93% of them were contaminated with microplastic particles.7. Contaminants are less present in glass bottles, suggesting that part of them comes from the packaging and the other part from the bottling process. Therefore, it is preferable to use filtration systems at home.
Several systems exist: filtration through different layers of rocks (as is the case in nature), gravity filtration through charcoal filters and polypropylene filters against heavy metals, reverse osmosis, and distillation, among others.
How to sort through these systems? It is advisable to avoid choosing a system with filters containing polypropylene, given the previously cited scientific studies on water from plastic bottles. Reverse osmosis and distillation are processes that allow for obtaining "pure" water, with very low mineral content, or even too low. Indeed, although these waters are pure, they are unstable: from an atomic point of view, the electrons in the outer shell tend to migrate towards the oxygen (O--), leaving the hydrogen (H+). This potential electronic "availability" makes the water molecule (H2O) very affine for multiple substances: in the body, it is eager for everything, both good and bad, in search of its stability. Thus, water that is too low in minerals can be used for cleansing treatments to act as a solvent. However, it should not be consumed exclusively every day, as it risks demineralizing the body in the long term.
How does water filtration occur naturally in nature?
Water on Earth is in constant circulation according to a cycle called the water cycle. Rainwater can be considered distilled water, as it originates from the evaporation of seawater and lake water due to the sun's heat, which then condenses in the cooler atmosphere and falls back down. When rain falls from the sky and saturates the ground, it flows and trickles through various layers (sand, pebbles, clay, humus, various rocks, etc.) where different filtration processes (physical, chemical, and biological) occur. It is thus filtered from various atmospheric impurities to become groundwater, naturally clean water. It is important to note that it is the combination of all the soil properties that allows this filtration. You can perform the following "home" experiment (which children will enjoy!) to illustrate the phenomenon: take three transparent containers and three funnels (or three plastic bottles cut in half to get the two previously mentioned parts). At the bottom of each funnel, place a piece of gauze from your first aid kit, then fill the first funnel with gravel, the second with sand, and the last with activated charcoal. Prepare "dirty" water by mixing water with soil (1 tablespoon per liter of water), a few small twigs, and small pebbles. You can also add a few drops of food coloring. Pour the same amount of "dirty" water into the three funnels, let the water flow through, and observe the result in the light. You will notice that the coarser debris like twigs and larger pebbles are blocked by all three types of filters (gravel, sand, and activated charcoal). However, the gravel filter lets the soil and coloring pass through, the sand filter traps most of the soil, and the activated charcoal does not trap the soil but removes some of the coloring. If you repeat the experiment by stacking the three filters (activated charcoal at the bottom, sand in the middle, and gravel on top), you will see that the filtration is much better because each layer has a specific function: mechanical filtration for gravel and sand, and chemical filtration by adsorption through the activated charcoal layer. In nature, this dual filtration is complemented by biological filtration thanks to plants and bacteria that develop on and in the soil. They absorb and transform some of the organic matter and pollutants carried by the water, such as nitrates, phosphates, heavy metals, etc.
Through this soil filtration process, the water also gains vitality by coming into contact with the minerals in the soil contained within various rocks (the vibrational rate will depend on the mineral composition of the water, the geographical filtration area, and the path taken by the water in vortex or spiral movements). This process makes the water molecules more linear and structured in such a way that they are more easily absorbable and better at hydrating. These vital water molecules will act on the body's ionization processes: all natural elements have an electrical value, and this is true for our cells with the transmembrane potential. Indeed, cells are positively charged on the outside and negatively charged on the inside, which generates a permanent current that only disappears upon the cell's death. This distribution of ions on either side of the cell's plasma membrane is made possible by the osmotic balance, which involves the movement of water between the intracellular and extracellular environments.
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or a molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons. The overall charge of the atom is neutral, with the positive charges of the protons balancing with the negative charges of the electrons. A negative ion comes from an atom that has gained one or more electrons. The oxygen molecule O2, which makes up 21% of the air we breathe (the rest being about 78% nitrogen and 1% other gases like water vapor, ozone, methane, or carbon dioxide), is an electrophilic molecule that easily acquires an additional electron to form the ion O2-. Air is naturally ionized, with a balance between positive and negative ions in natural spaces. In some natural spaces, large quantities of negative ions can be found: at the base of waterfalls, the breaking of water droplets releases electrons (a physical phenomenon called the Lenard effect) which ionize the oxygen (ion O2- described above). Other natural phenomena promote the creation of negative ions, such as showers or thunderstorms (the combination of factors influences the density and polarity of ions, which was very well studied notably by Norinder and Siksna in the years 1950 and 1951). Thus, large quantities of negative ions can be found in the mountains, by the sea, in forests, in the sun, etc.
Clarence Weston Hansell (1898 - 1967), an American research engineer, is probably the first to have been interested in the biological effects of ionic air (negative and positive ions) in the 1930s. He obtained more than 300 American patents on various subjects. During his research on ionized air, he noticed that the mood of one of his colleagues changed in response to the ions generated by their equipment. He discovered that his colleague was jovial when the machine produced negative ions and morose when it produced positive ions. His pioneering work has since been validated by more recent studies: negative ions are believed to be beneficial in combating depression.8,9 (seasonal and non-seasonal) by influencing the secretion of serotonin, as chemical antidepressant medications do.
The Russians have been using the benefits of negative ions in their medicine for a long time and have noticed significant effects on lung infections (notably bronchitis and asthma), blood pressure, healing, overall body metabolism, body temperature, blood and tissue oxygenation, inflammations, etc. The most common sensations reported in experiments with positive ions in the air are dryness and irritation of the nose, and headaches, whereas negative ions are associated with relaxation and a general cooling effect.10.
According to Pierce J.Howard, PhD and research director at the Centre des Sciences Cognitives Appliquées In Charlotte, North Carolina, USA, "generally speaking, negative ions increase the flow of oxygen to the brain, resulting in greater alertness, reduced drowsiness, and more mental energy.".
This helps us better understand the impact of external positive or negative ions, as well as the role of water, on our metabolic functions!
Thus, the NATURALIZER filter seems to be the best choice!
It is an ecological filter containing only natural components that mimic the filtration of water in the volcanic soil of the Japanese archipelago: a true volcanic spring water – negatively charged water – to drink at home every day. The first model was developed in 1980 and updated in 2014 to increase the filtration capacity: 200,000 liters, with a flow rate of 5 liters per minute.
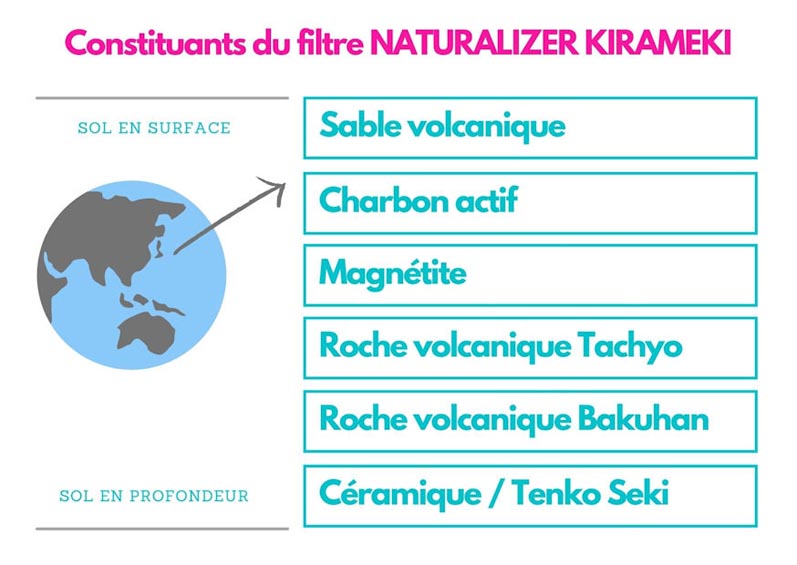
The Naturalizer filter is composed of six different natural materials arranged in nine successive layers, allowing it to deliver high-vibration pure mountain water. The system filters out chlorine residues present in tap water. Indeed, the best water on earth comes from the great depths of natural, free-flowing wild springs. This water is cleansed by rocks in a natural cleaning action before joyfully springing to the earth's surface, ready to be consumed.
He has been the subject of scientific and medical studies in Japan and then in the United States.
In Japan, the Japanese Ministry of Health has concluded that the regular consumption of water filtered by the Naturalizer filter reduces the possible harmful effects of tap water and provides water with properties beneficial to health for both internal and external use. It is now installed in more than thirty hospitals and clinics in Japan in its high-capacity "community" version and is even reimbursed by some Japanese health insurance companies when prescribed by a doctor.
In the United States, the Hippocrates Health InstituteHippocrates Health Institute) has adopted it since 2001 and has observed its benefits on patients, particularly on blood quality (monitored by regular blood count tests which showed an increase in the number of red blood cells and a slight increase in hemoglobin levels) thanks to its strong antioxidant properties. The center emphasizes the importance of water quality, particularly in contributing to the absorption of nutrients at the cellular level.
This filter, in addition to its inherent advantages and longevity, remains a very practical ecological option for daily use, as the filtration is done directly by simply operating the small lever on the faucet head. No storage, no daily production limit, no cartridges to change, fresh, lively, and vitalized water directly from the tap, available for the whole family.
1Emunctory: refers to an organ or part of an organ that allows the body to eliminate its waste.
2Vincent's Bioelectronics (BEV) was created by Louis-Claude Vincent in 1948 in France to objectively measure the quality of aqueous products and physiological fluids of the human body (blood, saliva, urine). "Biocompatible" means compatible with life, in order to fulfill its vital role by allowing physiological functions to be carried out.
3The rH2 indicates the oxidizing or reducing power of a solution. It refers to the dihydrogen potential. The rH2 scale ranges from 0 to 42: from 0 to 14, the environment is very antioxidant; from 14 to 28, the environment is antioxidant; from 28 to 42, the environment is oxidizing. Therefore, it is desirable to always have an rH2 below 28.
4"Blood trihalomethane levels and the risk of total cancer mortality in US adults." Min JY, Min KB. Environmental Pollution. 2016 May;212:90-96.
5"Cancer incidence and trihalomethane concentrations in a public drinking water system." Carlo GL, Mettlin CJ. American Journal of Public Health. 1980 May;70(5):523-5.
6"Microplastic contamination of drinking water: A systematic review" Evangelos Danopoulos et al. PLoS One. 2020 Jul 31;15(7):e0236838.
7"Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water," Sherri A Mason et al. Frontiers in Chemistry. 2018 Sep 11;6:407.
8"A Controlled Trial of Timed Bright Light and Negative Air Ionization for Treatment of Winter Depression," Michael Terman, Jiuan Su Terman, Donald C. Ross. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1998;55(10):875-882.
9"Controlled trial of bright light and negative air ions for chronic depression," Namni Goel et al. Psychological Medicine, 2005 Jul; 35(7): 945-55.
10"Air ions and respiratory function outcomes: a comprehensive review," Dominik D Alexander et al. Journal of Negative Results in Biomedicine, 2013 Sep 9;12:14.



